HistogramEqualize Class
This class enables you to apply histogram equalization algorithm.
Namespace:
Aurigma.GraphicsMill.Transforms
Assembly:
Aurigma.GraphicsMill (in Aurigma.GraphicsMill.dll)
Syntax
Public NotInheritable Class HistogramEqualize _ Inherits PerChannelBitmapTransform
public sealed class HistogramEqualize : PerChannelBitmapTransform
Remarks
Histogram equalization algorithm is used to automatically enhance a contrast of the image. As usual it makes the image too posterized, that's why it is seldom used to with photos (you should use Contrast effect with Auto property set to true). However it suits for scientific tasks (as a preparation before applying some specific algorithm like vectorization, recognition, etc).
Main idea of this algorithm is to build such look-up table (LUT) which makes the bitmap histogram equalized (all histogram entries are equal each other). Actually the histogram is never equalized absolutely, however this algorithm makes it as much as possible. After that this LUT is applied using ApplyLut class.
This class enables you to use not only histogram of the source bitmap, but any other histogram too. In this case algorithm will build the LUT for this histogram, but apply this LUT on the source bitmap. To specify another histogram, use property Histogram. If you want to get histogram from the bitmap automatically, set null to this property.
As long as this class is inherited from PerChannelBitmapTransform class, you can equalize histogram for specific channels. Just use Channels property, SelectAllChannels(), and DeselectAllChannels() methods in the common way for this.
Inheritance Hierarchy
Thread Safety
Static members of this type are safe for multi-threaded operations. Instance members of this type are safe for multi-threaded operations.Object Model

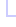

Supported Pixel Formats
| Member Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Format8bppGrayScale | 8 bits per pixel. Grayscale. 8 bits are used for luminosity level. |
| Format16bppGrayScale | 16 bits per pixel. Grayscale. All 16 bits are used for luminosity level (extended pixel format). |
| Format16bppAGrayScale | 16 bits per pixel. Grayscale with alpha channel. 8 bits are used for alpha channel and other 8 bits are used for luminosity level. |
| Format32bppAGrayScale | 32 bits per pixel. Grayscale with alpha channel. 16 bits are used for alpha channel and other 16 bits are used for luminosity level (extended pixel format). |
| Format24bppRgb | 24 bits per pixel. RGB. 8 bits each are used for the red, green, and blue components. |
| Format32bppRgb | 32 bits per pixel. RGB. 8 bits each are used for the red, green, and blue components. The rest 8 bits are unused. |
| Format32bppArgb | 32 bits per pixel. RGB with alpha channel. 8 bits each are used for the alpha, red, green, and blue components. |
| Format48bppRgb | 48 bits per pixel. RGB. 16 bits each are used for the red, green, and blue components (extended pixel format). |
| Format64bppArgb | 64 bits per pixel. RGB with alpha channel. 16 bits each are used for the alpha, red, green, and blue components (extended pixel format). |
| Format32bppCmyk | 32 bits per pixel. CMYK. 8 bits each are used for the cyan, magenta, yellow, and black components. |
| Format64bppCmyk | 64 bits per pixel. CMYK. 16 bits each are used for the cyan, magenta, yellow, and black components (extended pixel format). |
| Format80bppAcmyk | 80 bits per pixel. CMYK with alpha channel. 16 bits each are used for the alpha, cyan, magenta, yellow, and black components (extended pixel format). |